This article is the second installment in our Wi-Fi Sensing myth-busting series, where we address common questions and clear up misconceptions about the technology. If you missed the first post—an introduction to what Wi-Fi Sensing is and why it matters—you can catch up here. In this follow-up, we take a closer look at some of the questions we hear most often, including whether special hardware is required and how Wi-Fi Sensing compares to traditional motion sensors.
Does Wi-Fi Sensing require special hardware, or does it work with my existing Wi-Fi devices?
In most cases, you don’t need to buy anything new. Wi-Fi Sensing is primarily a software innovation that can often run on the Wi-Fi devices you already have in your home—such as routers, gateways, or other connected hardware—once the technology is integrated onto those devices. If your service provider offers services powered by WiFi Motion, you’ll have the ability to turn it on or off through their settings, giving you full control over when sensing is active. Instead of adding cameras or physical sensors to every room, these everyday devices become motion sensors, turning your home network into a sensing system. To make WiFi Motion accessible even for partners without a Wi-Fi Sensing–capable access point, Cognitive has also integrated the technology into WiFi Motion smart plugs. These plugs connect to the home’s Wi-Fi and act as their own motion sensing network, giving service providers a simple, turnkey way to deploy sensing capabilities.
How is Wi-Fi Sensing different from traditional motion sensors?
Traditional motion sensors—such as infrared (PIR), ultrasonic, or camera-based systems—each have strengths but also clear limitations. PIR sensors are a one-time purchase and fairly affordable, but they only work when they have a clear line-of-sight—meaning there can’t be walls or large obstacles in the way—and they’re often triggered by pets. Ultrasonic sensors can cover wide areas but may struggle with environmental noise. Cameras provide visual detail but raise privacy concerns and usually need good lighting to work effectively. Wi-Fi Sensing works differently: it interprets subtle changes in the Wi-Fi signals already in your home to detect motion. This allows it to cover broader spaces, even through walls or in low-light conditions, without requiring extra devices. It’s also privacy-friendly, detecting patterns of movement without capturing images or audio, making it a more adaptable and unobtrusive alternative. Wi-Fi Sensing can work together with traditional systems, using cameras in common areas where privacy is less of a concern while maintaining coverage in sensitive spaces like bedrooms or bathrooms where video or audio monitoring would be too intrusive. You can read more about the differences between PIR sensors and Wi-Fi Sensing, in our blog that contrasts them here.
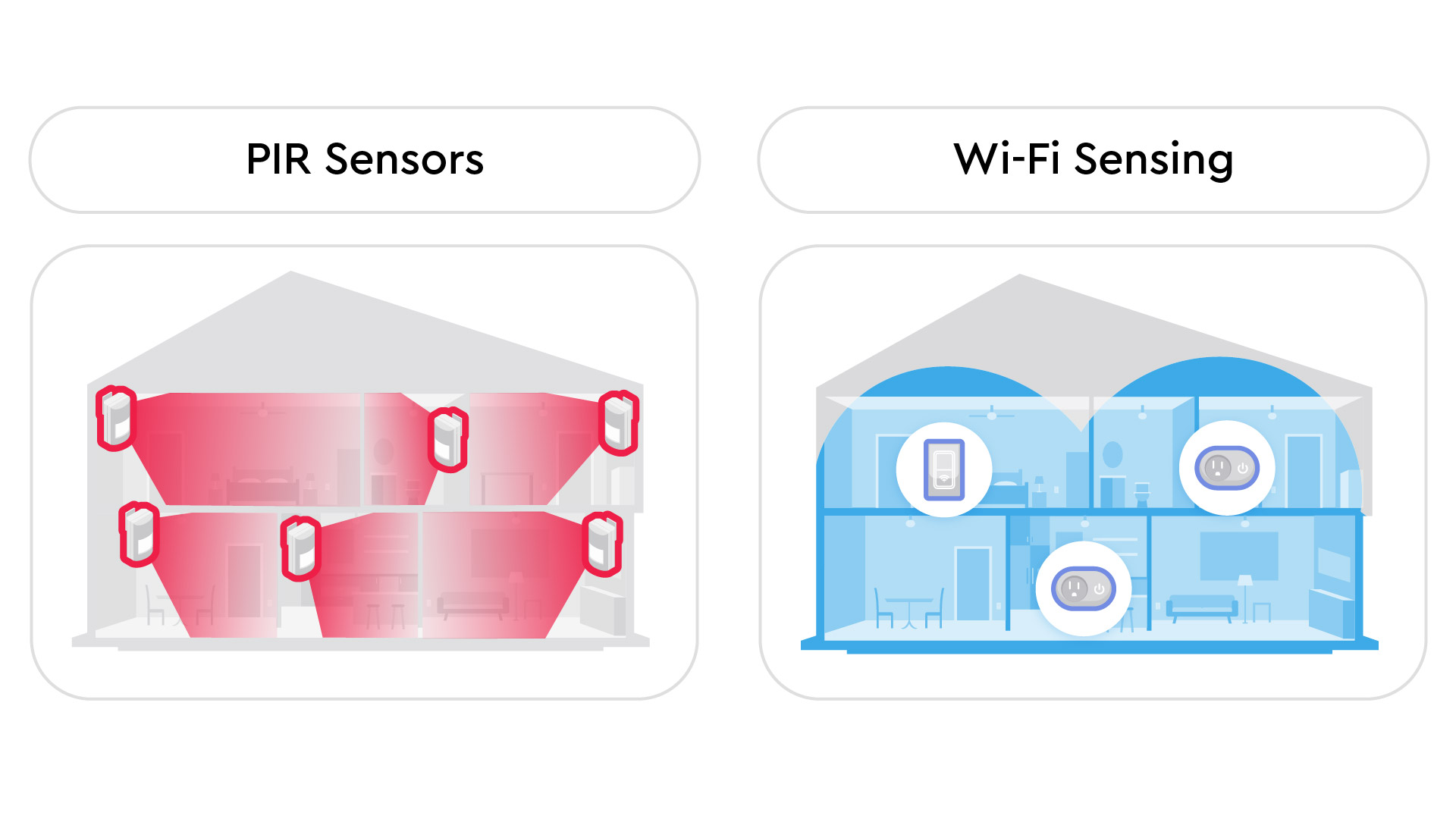
Comparison of the number of devices needed for complete motion sensing coverage
Can Wi-Fi Sensing detect more than one person moving at the same time?
Yes. Because Wi-Fi Sensing looks at the overall Wi-Fi environment, it can pick up multiple motion events happening at once. While it doesn’t identify who is moving, it can distinguish motion in different rooms or areas, giving you a clearer and more complete picture of activity throughout the home. However, it should be noted that some features, such as detecting the first motion of the day or sleep interruptions, reflect combined movement from multiple people rather than a single individual.
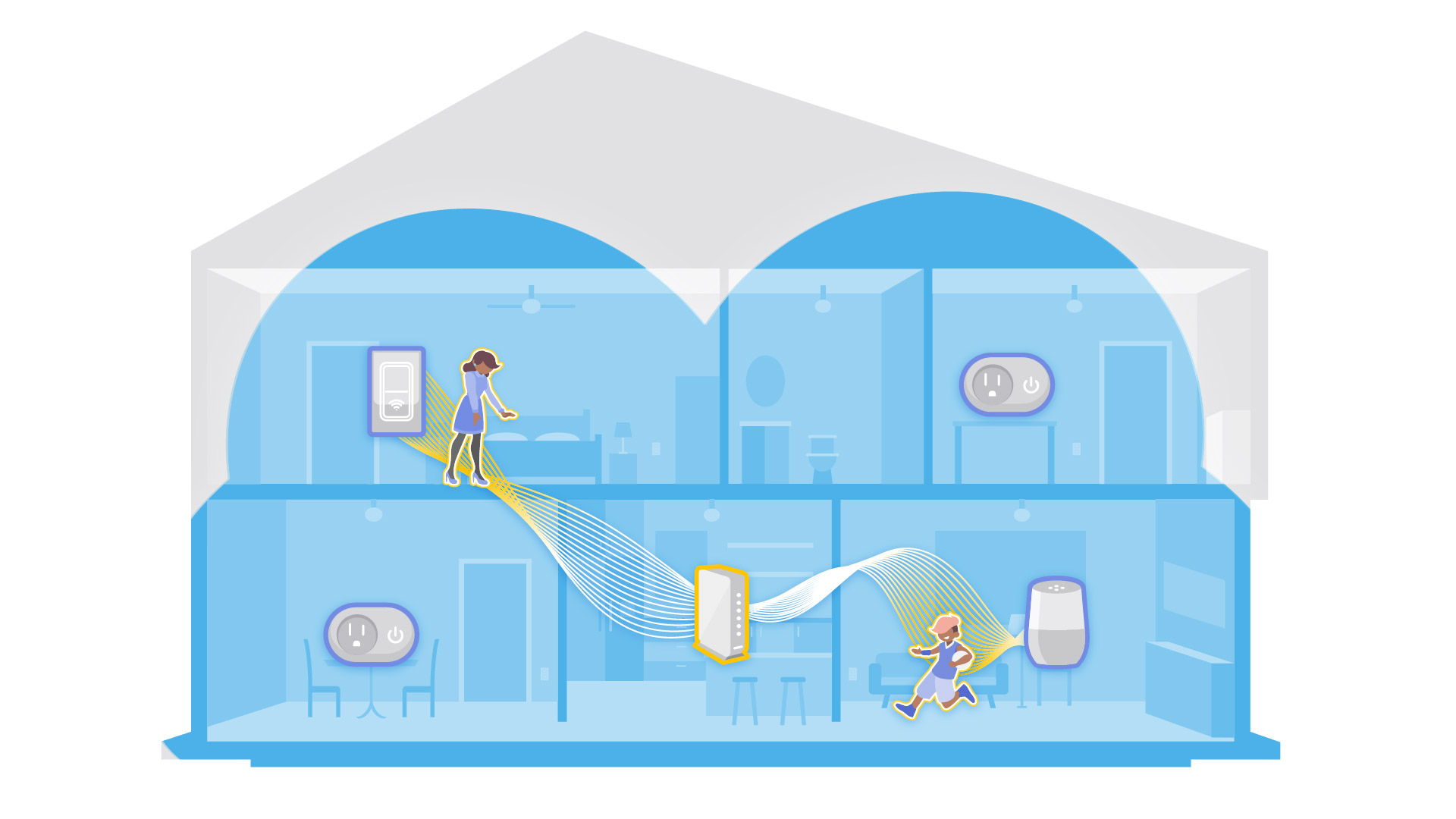
Wi-Fi Sensing can detect motion anywhere in the home that it has coverage, including multiple instances at once
Does Wi-Fi Sensing work through walls or only in the same room?
Wi-Fi signals naturally pass through walls, ceilings, and floors, which means Wi-Fi Sensing can detect motion across multiple rooms and even levels of a home. However, Wi-Fi Sensing depends on the quality of your Wi-Fi signal, which is typically measured by factors like RSSI (signal strength) and SNR (signal-to-noise ratio). Areas with weak signal quality may be harder to monitor reliably. To improve coverage, you can use mesh extenders to boost your Wi-Fi signal, and then strategically place connected devices like smart plugs or smart speakers so the sensing network can better detect motion throughout the home. To better understand sensing coverage, check out our blog on how to optimize coverage.
How can Wi-Fi Sensing tell where motion is happening?
Wi-Fi Sensing uses a process called localization. During setup, we recommend that service providers allow users to assign which connected devices—like routers, gateways, or smart plugs—will act as motion sensors and then organize them into “Rooms” within the app (for example, “Kitchen” or “Hallway”). When motion occurs, advanced algorithms analyze which devices exchanged Wi-Fi signals that were disrupted and match the event to the labeled room.
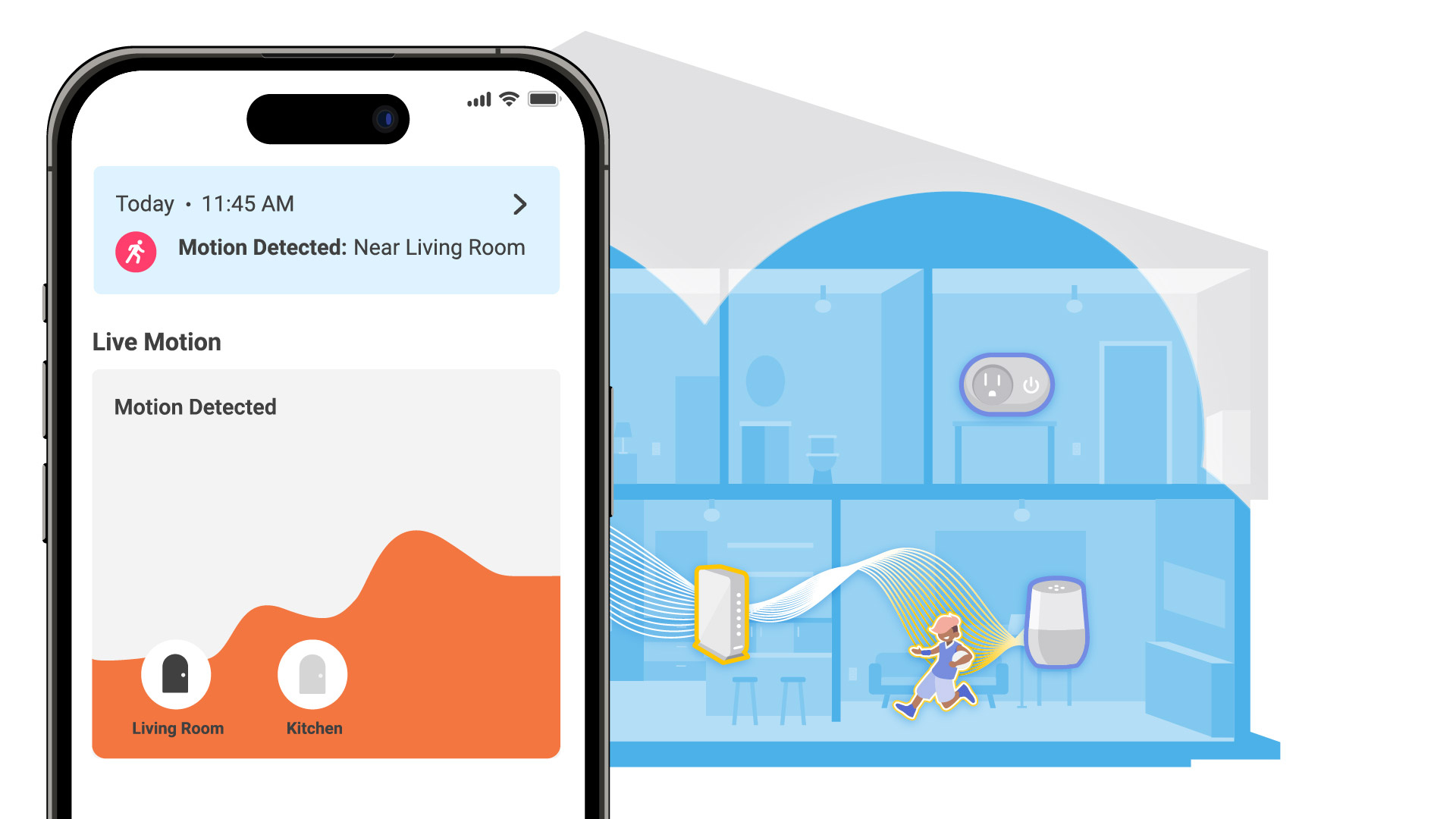
An example of Wi-Fi Sensing localization based on nearby connected devices
Does Wi-Fi Sensing impact my internet speed or performance?
No. Wi-Fi Sensing doesn’t stream or transfer extra data—it simply interprets the Wi-Fi activity that’s already happening between devices. The sensing runs quietly in the background without slowing down your internet connection.

